Empowering Solutions for
Your Aging Spine Patients
Your Aging Spine Patients
Traditional Posterior Fixation
Stabilization by Subtraction
Traditional fixation does achieve clinical goals but not without unintended consequence.
- Rigid fixation can lead to:
- Stiffness of the instrumented segments1
- Stress concentration of implants1
- Stress shielding of interbody space
- Adjacent segment disease and hardware related discomfort may occur2
- Fixation and stability in patients with poor bone quality can be challenging
- Screws loosening rates are >60% in osteoporotic bone3
- Mal-positioning of screws can lead to neurological damage and reoperations

Pierce Nunley M.D., Shreveport, LA
“Karma is not just another iteration of a procedure or device. This is innovation in the true sense of the word — it is disruptive and improves the lives of our patients.”
Aging Spine Paradigm Shift
Fixation with Anatomical Preservation
Karma can be used to achieve the clinical goals of traditional fixation without the unintended consequences.
- Karma is a novel metal-free, cortico-pedicular posterior fixation system
- MIS and open procedures are reproducible and straightforward
- Patient-centric implant
- Metal-free with minimal radiologic artifact
- Preserves the native posterior anatomy
- Minimal implant density
- Physiologically designed – positioned close to native IAR
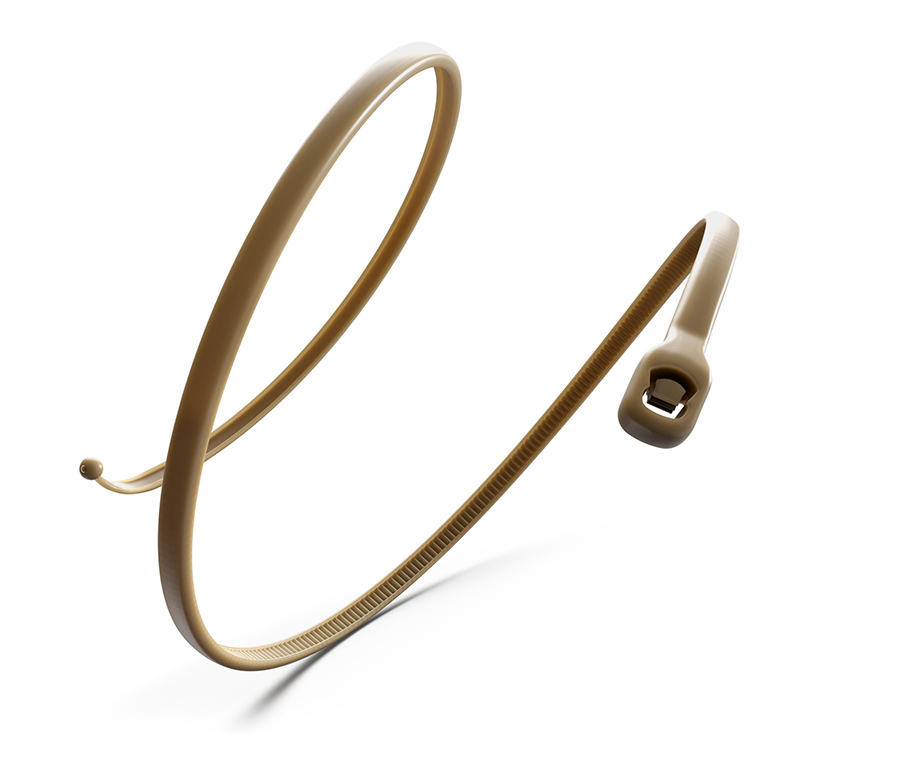

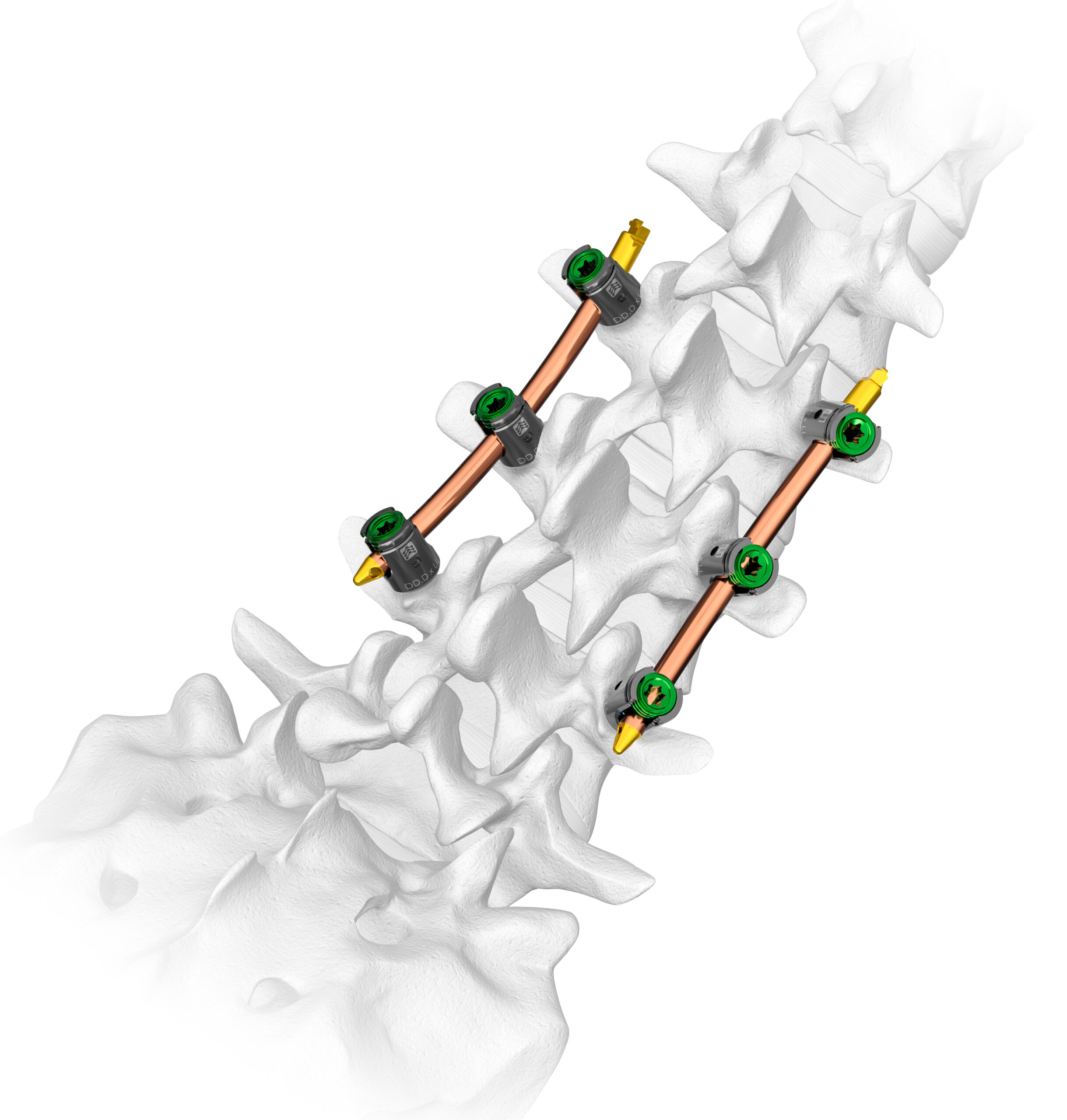
Multiple Fixation Points
Strong and Stable Cortical Fixation
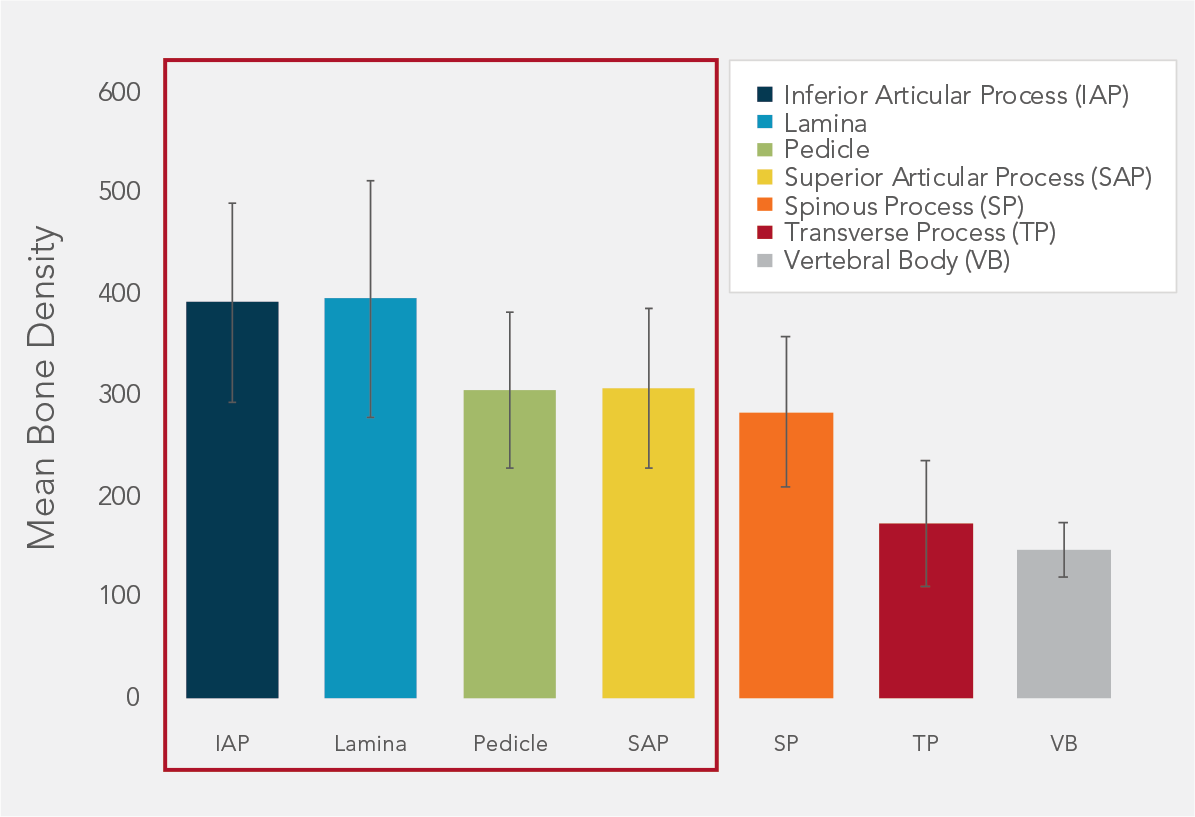
- Lumbar cortical density and thickness are greater in the posterior elements4
- Cortical fixation can be a reliable alternative to patients with poor bone quality
- Karma utilizes the four points of fixation that have the most Bone Mineral Density – IAP, SAP, Pedicle, Lamina
- Unlike pedicle screws Karma does not use the vertebral body which has the least Bone Mineral Density

Brian Anderson, M.D., MHA, Lehi, UT
“The Karma fixation system represents a significant advancement in the treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis and stenosis…”
Clinical Relevance
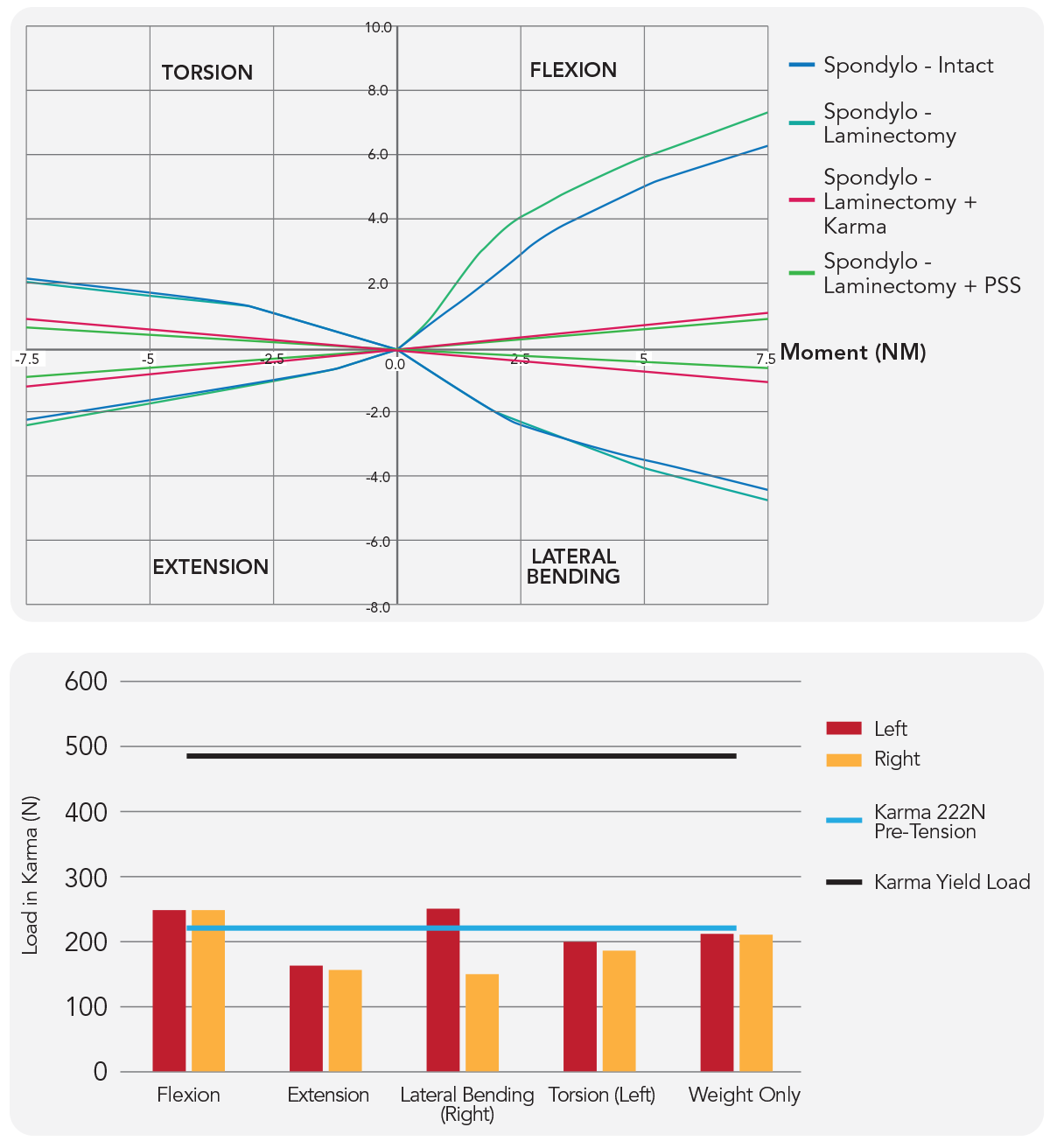
FEA Study Karma vs Pedicle Screws in Degenerative Spondylolisthesis7
- Bone and ligament resection associated with a laminectomy procedure results in a small increase in range of motion compared to intact (~1º in flexion)
- Both Karma and PSS significantly decrease ROM compared to intact and laminectomy models
- Difference in ROM between Karma and PSS is negligible
- In all modalities at maximum loading, tensile forces in Karma remained below the yield load

Terrence Crowder M.D., Gilbert, AZ
“Those with severe leg pain (neurogenic claudication or radiculopathy) and degenerative spondylolisthesis are ideal for this device. It’s fantastic that…”
- Liu et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:231 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-2132-5.
- Hsieh et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2020) 21:100 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-020-3111-1.
- Kafchitsas et al. The impact of surgical fixation technique on pedicle screw anchorage; SENSE Presentation June 2022 Literature Review 43 full papers Reviewed.
- Pedicle Screws Challenged: Lumbar Cortical Density and Thickness are Greater in the Posterior Elements Than in the Pedicles. Khalid Odeh, MD, Alexander Rosinski, MS, Jeremi Leasure, MSE, and Dimitriy Kondrashov MD. Global Spine Journal (AO spine) 1-10 2019.
- Evaluation of the ability of a novel curved drill to create an arcuate tunnel without breaching the spinal canal. SMISS 2021. Eastlack et al.
- A Biomechanical Comparison of Stability and Anterior Column Load Sharing: Transfacet – Intralaminal Cortical Fixation versus Traditional Pedicle Screw Instrumentation after Lateral Interbody Fusion, SMISS 2022 Eastlack et al.
- Kepler, C. (2023). Finite element analysis comparing a PEEK posterior fixation device versus pedicle screws for lumbar fusion in a Degenerative Spondylolisthesis model with Laminectomy [Manuscript submitted for publication] Rothman Orthopedics, Philadelphia, PA, USA.
